Code 401 - Read 35 - Graphs
Introduction
A Graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of a finite set of vertices (nodes) and set of edges which connect a pair of nodes.
Graphs are used to represent networks, like a telephone network or a circuit network. Graphs are also used in social media networks. For example, in Facebook, each person is represented with a vertex that contains information like the person’s id, name, gender, friends list etc.
Terminology
Vertex - a node - data object that can have zero or more adjacent vertices. Edge - a connection between two vertices. Neighbor - the vertex’s adjacent vertices (connected to it by edges). Degree - the number of edges connected to that vertex.
Graph Types
Directed vs Undirected
An Undirected Graph is a graph where each edge is undirected or bi-directional, and it doesn’t move in any direction.
A Directed Graph (Digraph) is a graph where every edge is directed; each vertex is directed at another vertex with a specific requirement of what vertex should be referenced next.

Complete vs Connected vs Disconnected
A Complete Graph is when all nodes are connected to all other nodes.
A Connected Graph is graph that has all of vertices have at least one edge. A Tree is a form of a connected graph.
A Disconnected Graph is a graph where some vertices may not have edges.
Acyclic vs Cyclic
A cycle is when a vertex can be traversed through and potentially end up back at itself.
An Acyclic Graph is a directed graph without cycles.
A Cyclic Graph is a graph that has cycles.

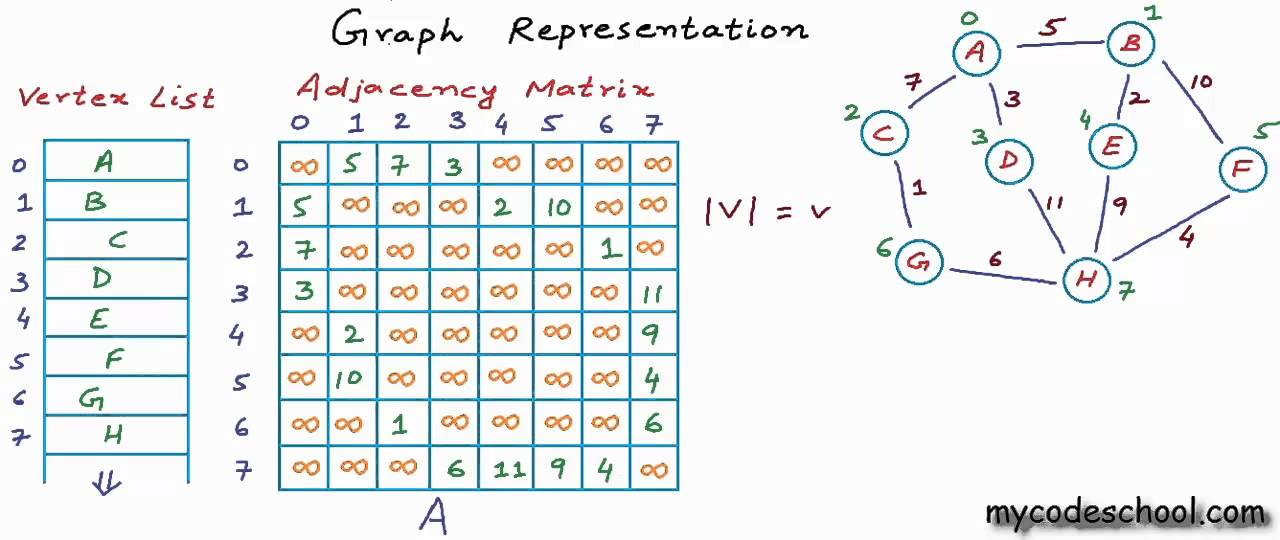
Graph Representation
Graphs can be represented through:
Adjacency Matrix
Its represented through a 2-dimensional array. If there are n vertices, then we are looking at an n x n Boolean matrix. Its faster (O(1) to find a vertex) but takes more space (O(N*N)).
Adjacency List
A collection of linked lists or an array that lists all of the other vertices that are connected. Adjacency lists make it easy to view if one vertices connects to another. Its a bit slower than the matrix but takes less space.
Weighted Graphs
It is a graph with numbers assigned to its edges. These numbers are called weights.
Real World Uses of Graphs
Few examples of graphs in use:
- GPS and mapping
- Driving directions
- Social media Networks
- Airline traffic