Code 401 - Read 10 - Stacks and Queues
Stacks
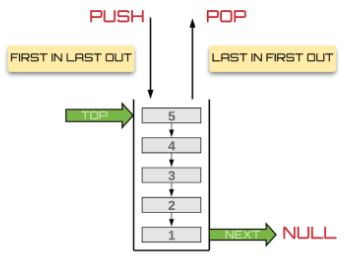
A stack is a container of objects that are inserted and removed according to the last-in first-out (LIFO) principle. Objects are called Nodes, where each Node references the next Node in the stack, but does not reference its previous.
Stacks common terminology
- Push - for adding Nodes to a stack
- Pop - for removing Nodes from a stack. Popping from an empty stack will raise an exception
- Top - the top of a stack
- Peek - the value of the top Node in a stack. Peeking an empty stack will raise an exception
- IsEmpty - returns true when stack is empty otherwise returns false.
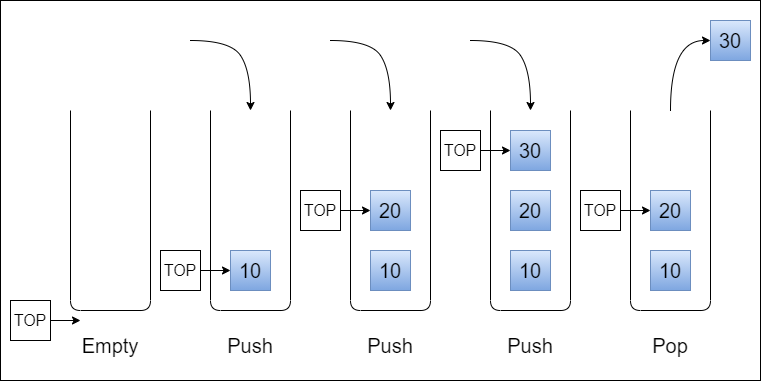
Stacks concepts
- Push -> FILO - First In Last Out: the first item added in the stack will be the last item popped out of the stack.
- Pop -> LIFO - Last In First Out: the last item added to the stack will be the first item popped out of the stack.
Pushing
To add a new Node to a stack, push it into the stack by assigning it as the new top, with its next property equal to the original top.
- Define the Node that you want to add
- Assign the next property of new Node to reference the same Node that top is referencing
- Re-assign the top so it references the new Node
This is an O(1) operation because it takes the same amount of time no matter how many Nodes there are in the stack.
Popping
To remove a Node from the top. When conducting a pop, the top Node will be re-assigned to the Node that lives below and the top Node is returned to the user.
- Check isEmpty to ensure no exceptions are raised. Alternately, you can wrap the call in a try/catch block
- Create a reference named temp that points to the same Node that top points to
- Re-assign top to the value that the next property is referencing
- Clear out the current temp next property
- Return the value of the temp Node
This is an O(1) operation because it takes the same amount of time no matter how many Nodes there are in the stack.
Peek
When conducting a peek, you will only be inspecting the top Node of the stack. Check isEmpty to ensure no exceptions are raised. Alternately, you can wrap the call in a try/catch block. This is an O(1) operation because it takes the same amount of time no matter how many Nodes there are in the stack.
IsEmpty O(1)
Check if the top is null. This is an O(1) operation.
Queues
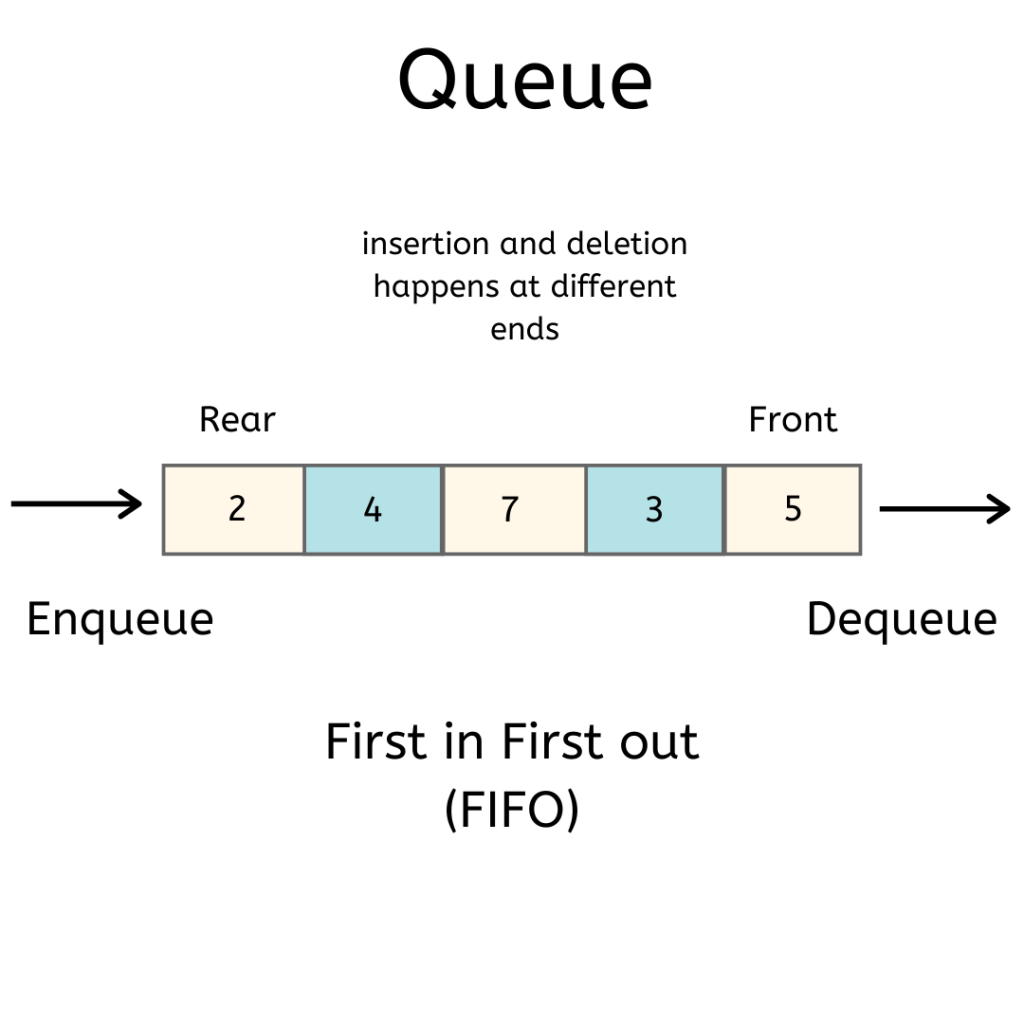
A queue is a container of objects (a linear collection) that are inserted and removed according to the first-in first-out (FIFO) principle.
Queues common terminology
- Enqueue - for adding Nodes to a queue
- Dequeue - for removing Nodes from a queue. Popping from an empty queue will raise an exception
- Front - the front/first Node of a queue
- Rear - the rear/last Node of a queue
- Peek - the value of the front Node in a queue. Peeking an empty queue will raise an exception
- IsEmpty - returns true when queue is empty otherwise returns false.

Queues concepts
- Push -> FIFO - First In First Out: the first item in the queue will be the first item out of the queue.
- Pop -> LILO - Last In Last Out: the last item in the queue will be the last item out of the queue.
Enqueue O(1)
To add an item to a queue, you use the rear next property.
Let’s walk through the process of adding a Node to a queue:
- Change the next property of the rear to point to the Node we are adding.
- Re-assign the rear reference to point to the new Node 5.
This is an O(1) operation in time because it does not matter how many other items live in the queue (n); it takes the same amount of time to perform the operation.
Dequeue
To remove an item from a queue:
1 Check isEmpty to ensure no exception are beinng raised. Alternately, you can wrap the call in a try/catch block
- Create a temporary reference type named temp and have it point to the same Node that front is pointing to
- Re-assign front to the next value that the Node front is referencing.
- Re-assign the next property on the temp Node to null
- Return the value of the temp Node that was just removed
This is an O(1) operation in time because it doesn’t matter how many other items are in the queue, you are always just removing the front Node of the queue.
Peek
When conducting a peek, you will only be inspecting the front Node of the queue. Check isEmpty to ensure no exceptions are raised. Alternately, you can wrap the call in a try/catch block. This is an O(1) operation because it takes the same amount of time no matter how many Nodes there are in the stack.
isEmpty
This is an O(1) operation because it takes the same amount of time no matter how many Nodes there are in the stack.
Stack vs Queue

| stacks | Queues |
|---|---|
| Based on the LIFO principle | Based on the FIFO principle |
| Pushing and popping takes place only from one end of the list | Enqueuing and Denqueuing takes place from the opposite ends of the list |
| Only one pointer is maintained to access the list (top) | Two pointers are maintained to access the list (front and rear) |
| Used in solving problems works on recursion | Used in solving problems having sequential processing |